การวิเคราะห์สหสัมพันธ์คาโนนิคอลระหว่างปัจจัยที่มีผลต่อการใช้เทคโนโลยีสำนักงานเสมือนจริงกับความผูกพันต่อองค์กรของพนักงานในอุตสาหกรรมขนส่งและโลจิสติกส์
คำสำคัญ:
คาโนนิคอล, สำนักงานเสมือนจริง, การทำงานทางไกล, ความผูกพันต่อองค์กรของพนักงานบทคัดย่อ
การวิจัยครั้งนี้มีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อศึกษาความสัมพันธ์คาโนนิคอลระหว่างปัจจัยที่มีผลต่อการใช้เทคโนโลยีสำนักงานเสมือนจริงกับความผูกพันต่อองค์กรของพนักงานในอุตสาหกรรมขนส่งและโลจิสติกส์ กลุ่มตัวอย่างที่ใช้ในการวิจัยคือพนักงานที่ปฏิบัติงานในอุตสาหกรรมขนส่งและโลจิสติกส์ที่ทำงานอยู่ภายใต้นโยบายสำนักงานเสมือนจริง ในเขตจังหวัดกรุงเทพฯและปริมณฑล จำนวน 400 คน โดยวิธีการสุ่มตัวอย่างแบบตามสะดวก ผู้วิจัยเก็บข้อมูลโดยใช้แบบสอบถามเป็นเครื่องมือ สถิติที่ใช้ในการวิเคราะห์ข้อมูลคือความถี่ ร้อยละ ค่าเฉลี่ย ส่วนเบี่ยงเบนมาตรฐาน และการวิเคราะห์สหสัมพันธ์คาโนนิคอล
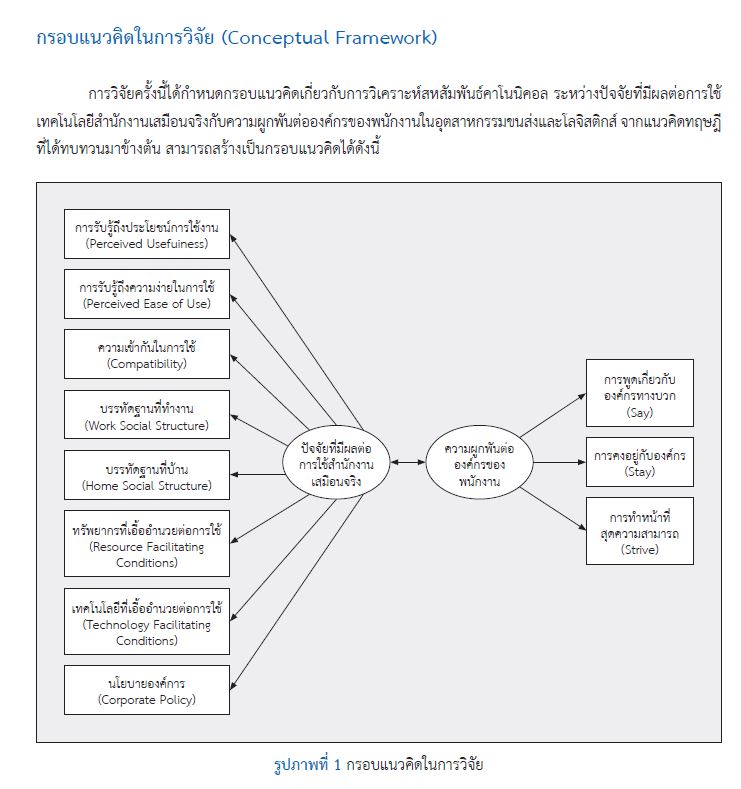
ผลการศึกษาพบว่า ปัจจัยที่มีผลต่อการใช้เทคโนโลยีสำนักงานเสมือนจริงมีความสัมพันธ์ในระดับสูงมากกับความผูกพันต่อองค์กรของพนักงานในอุตสาหกรรมขนส่งและโลจิสติกส์ (สัมประสิทธิ์คาโนนิคอล เท่ากับ .727) ปัจจัยที่มีผลต่อการใช้เทคโนโลยีสำนักงานเสมือนจริงมีค่าน้ำหนักความสำคัญคาโนนิคอลระหว่าง .538 - .811 โดยกลุ่มตัวอย่างให้ความสำคัญกับการรับรู้ถึงความง่ายในการใช้เทคโนโลยีสำนักงานเสมือนจริงมากที่สุด ส่วนปัจจัยด้านความผูกพันต่อองค์กรของบุคลากรมีค่าน้ำหนักความสำคัญคาโนนิคอลระหว่าง .564 - .764 โดยกลุ่มตัวอย่างให้ความสำคัญกับการคงอยู่กับองค์กรมากที่สุด แสดงให้เห็นว่าในการดำเนินนโยบายการนำเทคโนโลยีสำนักงานเสมือนจริงมาใช้งานในองค์กร ผู้บริหารองค์กรจำเป็นที่จะต้องคำนึงถึงความง่ายของการใช้เทคโนโลยีสารสนเทศในการปฏิบัติงานของบุคลากร รวมถึงการช่วยสนับสนุนทั้งอุปกรณ์ สิ่งอำนวยความสะดวก และทรัพยากรต่าง ๆ ที่จะทำให้บุคลากรสามารถปฏิบัติงานที่ได้รับมอบหมายของตนเองให้สำเร็จลุล่วงอย่างมีประสิทธิภาพได้ บุคลากรจึงจะรู้สึกว่าเทคโนโลยีนั้น ๆ เป็นเครื่องมือที่ช่วยสนับสนุนการปฏิบัติงานของตน ก่อให้เกิดความพึงพอใจในงานและนำไปสู่ความผูกพันต่อองค์กรของพนักงานในที่สุด
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Ajzen, I. (1985). From Intentions to Actions: A Theory of Planned Behavior. Springer: Heidelberg.https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-69746-3_2
Ajzen, I. (1991). The theory of planned behavior. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 50(2), 179–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/0749-5978(91)90020-T
Ajzen, I. (2002). Perceived behavioral control, self-efficacy, locus of control, and the theory of planned behavior. Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 32(4), 665–683. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1559-1816.2002.tb00236.x
Blaique, L., & Pinnington, A. (2023). Virtual work challenges and opportunities in the Asia-Pacific region: the role of organizational virtual work climate. Elgar Companion to Managing People Across the Asia-Pacific, 269-288. https://doi.org/10.4337/9781802202250.00023
Clark II, S. D., & Olfman, L. (1999). Influencing the decision to telework—testing the simplified decision model. In Proceedings of the 1999 ACM SIGCPRconference on Computer personnel research, 65-72. https://doi.org/10.1145/299513.299618
Cochran, W. G. (1953). Sampling Techniques. New York: John Wiley & Sons.Grant.
Grant, C.A., Wallace, L.M., Spurgeon, P.C., Tramontano, C. & Charalampous, M. (2019). Construction and initial validation of the E-Work Life Scale to measure remote e-working. Employee Relations, 41(1), 16-33.https://doi.org/10.1108/ER-09-2017-0229
Debbie, D. D., & Carol, M. L. (2016). Managing Virtual Teams. New York: Business Expert Press, LLC.
Haines, V. Y. III, St-Onge, S., & Archambault, M. (2002). Environmental and person antecedents of telecommuting outcomes. Journal of Organizational and End User Computing, 14(3), 32–50.https://doi.org/10.4018/joeuc.2002070103
Harunavamwe, M. & Kanengoni, H. (2023), Hybrid and virtual work settings; the interaction between technostress, perceived organizational support, work-family conflict and the impact on work engagement. African Journal of Economic and Management Studies. https://doi.org/10.1108/AJEMS-07-2022-0306
Igbaria, M., & Guimaraes, T. (1999). Exploring Differences in Employee Turnover Intentions and Its Determinants Among Telecommuters and Non-Telecommuters. Journal of management Information Systems, 16(1), 147-164. https://doi.org/10.1080/07421222.1999.11518237
Johansen, B. & Euchner, J. (2013), Conversations: navigating the VUCA world: an interview with Bob Johansen. Research-Technology Management, 56(1), 10-15. https://doi.org/10.5437/08956308X5601003
Lubowiecki-Vikuk, A., Budzanowska-Drzewiecka, M., Borzyszkowski, J. & Taheri, B. (2023). Critical reflection on VUCA in tourism and hospitality marketing activities. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 35(8), 2983-3005. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJCHM-04-2022-0479
Maharani, A. (2024). Back to Work or Remote Work: Trends and Challenges. Business and Management in Asia: Disruption and Change, 139-150. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-9371-0_9
Mann, S., & Holdsworth, L. (2003). The Psychological Impact of Teleworking: Stress, Emotions and Health.
New technology, work and employment, 18(3), 196-211. https://doi.org/10.1111/1468-005X.00121
Mello, J. A. (2007). Managing Telework Programs Effectively. Employee Responsibilities and Rights Journal, 19(4), 247–261. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10672-007-9051-1
Mathasit Tanyarattanasrisakul. (2016). The Canonical Correlation Analysis for Educational Mathematics. Mathematical Journal by The Mathematical Association of Thailand Under the Patronage of His Majesty the King, 61(690), 13 -26.
Marketeer Magazine. (2021). The parcel delivery market is growing, each brand must adjust their strategies to speed up and escape competitors in terms of both price and speed. from URL Address https://marketeeronline.co/archives/222852.
Nilles, J. M. (1988). Traffic Reduction by Telecommuting: A Status Review and Selected Bibliography. Transportation Research Part A: General, 22(4), 301–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/0191-2607(88)90008-8
Olsen, K.M., Hildrum, J., Kummen, K. & Leirdal, C. (2023). How do young employees perceive stress and job engagement while working from home? Evidence from a telecom operator during COVID-19. Employee Relations, 45(3), 762-775. https://doi.org/10.1108/ER-05-2022-0230
Sherry, A. & Henson, R. K. (2005). Conducting and Interpreting Canonical Correlation Analysis in Personality Research: A User-Friendly Primer. Journal of Personality Assessment, 84(1), 37-48.https://doi.org/10.1207/s15327752jpa8401_09
Schutz, D.P., & Schutz, S.E. (1994). Psychology and Work Today: An Introduction to Industrial and Organization Psychology. Macmillan.
Sparrow, P. (2000). New employee behaviours, work designs and form of work organization: what is in store for the future of work?. Journal of managerial, 15, 202-218.https://doi.org/10.1108/02683940010320561
Steers, R. M. (1977). Organization Effectiveness. California: Goodyear Publishers Inc.
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
รูปแบบการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2024 คณะบริหารธุรกิจ สถาบันบัณฑิตพัฒนบริหารศาสตร์

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.



